Nicotine Dependence Level among Adult Male Smokers Living in North Okkalapa Township, Yangon, Myanmar
Abstract
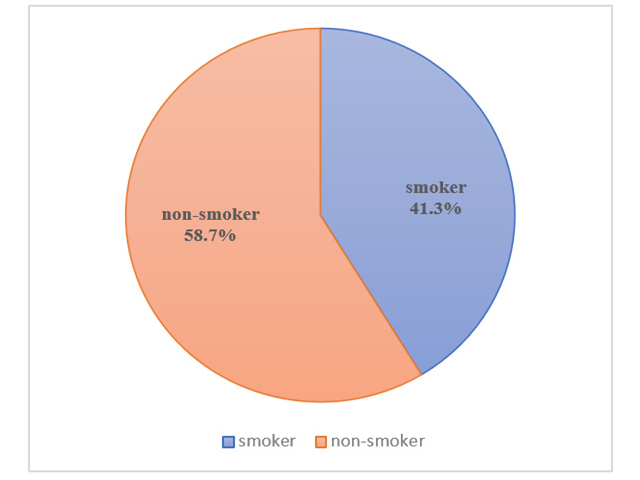
Background and Aim: This study determined nicotine dependence level among adult male smokers living in North Okkalapa Township, Yangon, Myanmar and association between socio-demographic characteristics and smoking status. Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional analytical study was carried out in adult male subjects (n=450) with the age between 18 and 40 years using multistage sampling method. These recruited participants were categorized into smokers and non-smokers according to their smoking history. Each smoker was interviewed by using standardized Myanmar version of Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence (FTND) to assess nicotine dependence level. Moreover, sociodemographic information, including age, marital status, and level of education (primary school, secondary school, high school and university), and occupational information (elementary class, middle class and high class) were collected using a self-designed questionnaire. Results: Among 450 adult male subjects, 264 (58.7%) were non-smokers, whereas 186 (41.3%) were smokers. Mean level of FTND score of smokers was 3.80±2.6. It was shown 33.3% for very low dependence, 22.0% for low dependence, 12.9% for moderate, 25.3% for high dependence as well as 6.5% for very high dependence. It had observed that nicotine dependence was significantly associated with marital status, level of education, pack year, age at smoking initiation and occupational status. Conclusion: Our results revealed some sociodemographic factors affecting nicotine dependence and showed that nicotine dependence is high in Myanmar's population. These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions and public health strategies to address nicotine dependence in Myanmar.
Copyright (c) 2025 Yin Thu Theint, Khin Thuzar Aung, Khin Mi Mi Lay, Mya Thanda Sein

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





