Effect of Oral Vitamin C Supplementation on Serum Interleukin 6, Hepcidin and Iron Status in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
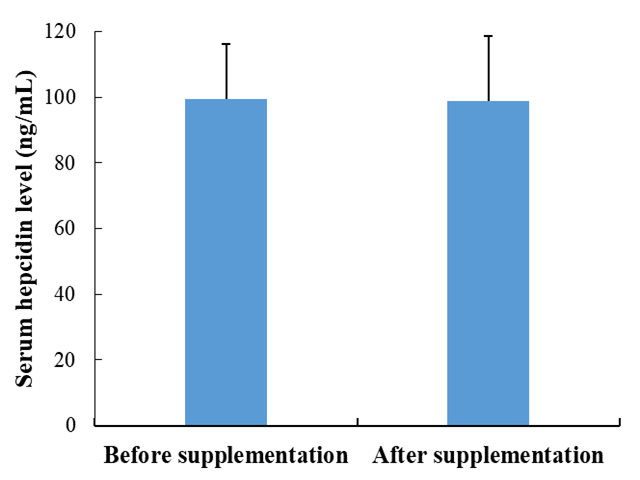
Background and Aim: Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM) with Metabolic Syndrome (Mets) is a chronic inflammatory state with an increased expression of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin 6 (IL-6). Iron regulatory peptide hepcidin secretion is also increased as IL-6 causes hepcidin secretion, leading to iron dysregulation. Vitamin C (L ascorbic acid) has potential effects in alleviating the inflammatory status. This study aimed to investigate the effect of vitamin C supplementation on serum interleukin 6 (IL-6), hepcidin, and iron status in T2DM patients with Mets. Methods: Total 76 patients with the age between 40-60 years according to Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III were selected and randomly assigned to supplement (vitamin C or placebo) groups using block randomization. Before and after 8-week supplementation of 250 mg vitamin C/placebo tablets for two times per day, serum Iron status, IL-6 and hepcidin levels were measured, using the colorimetric and the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Results: In both groups, serum IL-6 level was significantly increased, ferritin level was significantly decreased after supplementation while changes in hepcidin levels were not statistically significant. Moreover, percent changes of all variables were not significantly different between groups. Conclusion: Vitamin C 250 mg two times per day for 8-week supplementation with could not provide beneficial effect to explore the anti-inflammatory effect in T2DM patients with metabolic syndrome.
Copyright (c) 2025 Aye Mya Mya Thwin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





