Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza Combined with Aromatic Amino Acids on the Impaired Renal Function in Rats with Chronic Renal Failure
Abstract
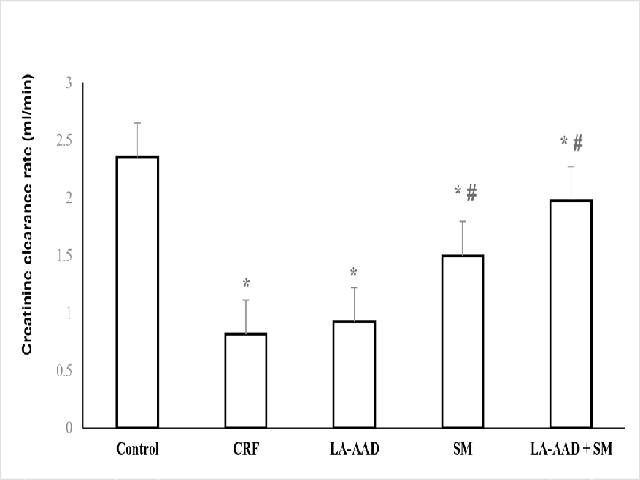
Background and Aim: At present, the main therapy for chronic renal failure (CRF) is dialysis and renal transplantation, but neither obtains satisfactory results. Salvia miltiorrhiza (SM) is a very popular medicinal plant that has been extensively applied to treat various diseases. It also has been reported that lowering the aromatic aminoacids (AAA) in the protein diet can improve renal function in rodents with CRF. This study seeks to employ the use of SM combined with low aromatic amino acid diet (LA-AAD) for treatment of CRF in rats. Methods: Animals were assigned into 3 groups: Control, CRF and Experiment. CRF models were induced by 2.5% adenine administered by gavage for 8 weeks. Control and CRF group received normal protein diet (18.8% proteins, AAA 0.024%), and Experiment group was divided into 3 subgroups, being treated with SM (1.0g/kg/d) and LA-AAD (18% proteins, AAA 0.009%) differently. Proteinuria, blood urine nitrogen (BUN), serum and urine creatinine (Scr, Ucr) were measured and creatinine clearance rate (CCR) was calculated accordingly. Results: Proteinuria, BUN, Scr analyses showed amelioration of functional parameters and increased the CCR significantly in LA-AAD + SM group. Conclusion: These results showed that the combination of SM and LA-AAD could be beneficial to the improvement of renal function in CRF rats and this method can be a novel strategy for CRF treatment.