Effect of 1/f Fluctuation Signal on the Slope of EEG α-α Interval Fluctuation
Abstract
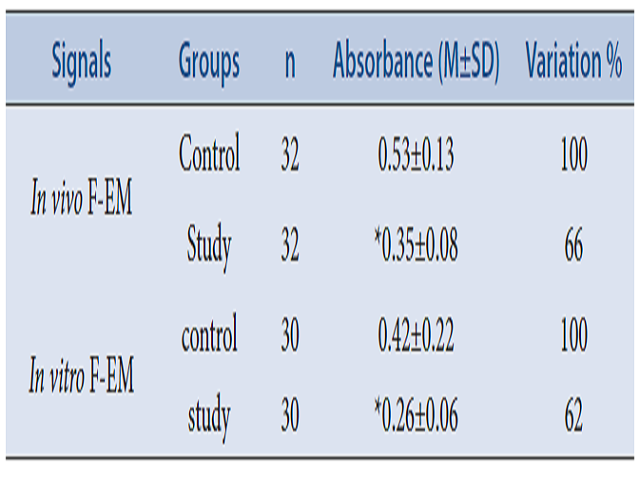
The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of 1/f fluctuation wave on EEG α-α interval and stability of cell membrane. We compared and analyzed the effect of 1/f fluctuation with different character of signal and slope on the fluctuation of EEG α-α interval in healthy men and grey rabbits, and studied the effect of 1/f fluctuation on the stability of cell membrane. Main outcome measures were EEG and stability of cell membrane. The gradient of EEG α-α interval fluctuation was increased to 142% by electromagnetic field with 1.5 of β value and to 135% by sound impulse with 1.5 of β value and character of 1/f. After 1/f fluctuation signal act, erythrocyte membrane osmotic resistance was increased by 34~38%. Sound wave and electromagnetic wave with property of 1/f fluctuation increase the gradient of EEG α-α interval fluctuation (β value) to the normal values. (b) Slope (β-value) of EEG α-α interval fluctuation is irritable (sharp) indicator reflecting condition of brain. (c) 1/f fluctuation signal increases the stability of cell membrane.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





