Swimming Helps Elderly Population to Improve Mental Speed and Attention
Abstract
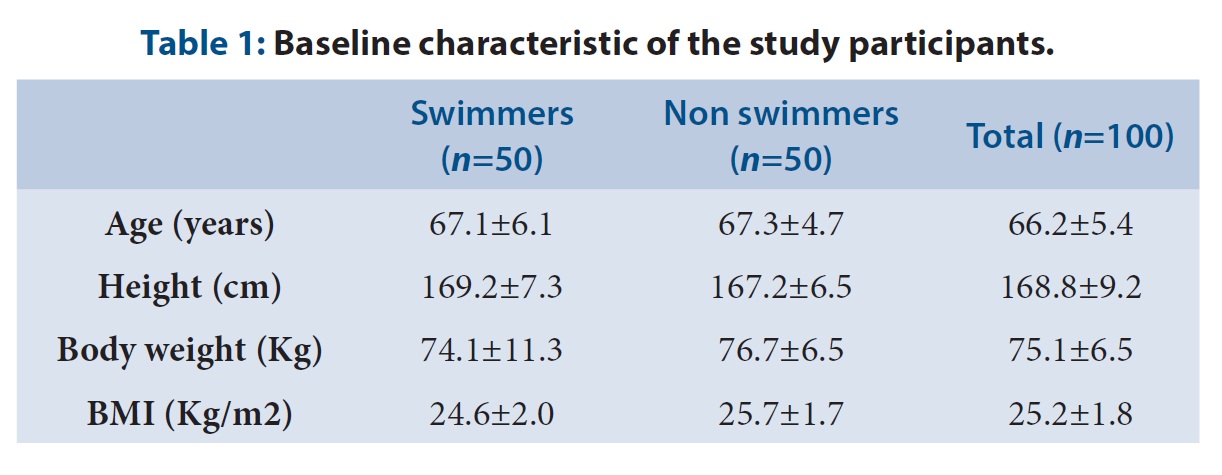
Background and Aim: Swimming is an ideal physical activity for the elderly population because of its low impact on joints and minimal risk of injury. Previous studies have proven that swimming has beneficial effect on skeletal and cardiovascular health. But studies to assess effects of swimming on cognitive health of elderly are lacking. Methods: This study was undertaken to assess and compare the level of cognition among elderly swimmers and non swimmers. 50 elderly subjects who regularly swim and 50 elderly non swimmers were recruited. Digit symbol substitution test and Digit vigilance test were done to assess the mental speed and attention of the subjects. Results: Results were statistically analyzed using students t test to compare between the groups. Swimmers took less time to complete both Digit symbol substitution test and Digit vigilance test than non swimmers. Conclusion: Elderly swimmers had better mental speed and attention compared to non swimmers.